India's whole-virion inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine shows promise
by Sally Robertson, B.Sc.Researchers in India have conducted a preclinical study demonstrating the safety and efficacy of a new candidate vaccine for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the agent that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
The vaccine is composed of an inactivated whole SARS-CoV-2 virion with one of two different adjuvants: either aluminum hydroxide gel (Algel) or a novel TLR7/8 agonist adsorbed Algel.
Krishna Mohan Vadrevu (Bharat Biotech International Ltd) and colleagues say both forms of the vaccine, called BBV152, induced high titers of neutralizing antibodies in mice, rabbits, and rats, without any safety concerns.
The formulation containing the TLR7/8 agonist also induced a distinct T helper cell 1 (Th1) biased antibody response with increased levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)+ CD4 cells.
The researchers say the findings provide evidence to support the testing of BBV152 in phase I clinical trials.
A pre-print version of the paper is available On the server bioRxiv*, while the article undergoes peer review.
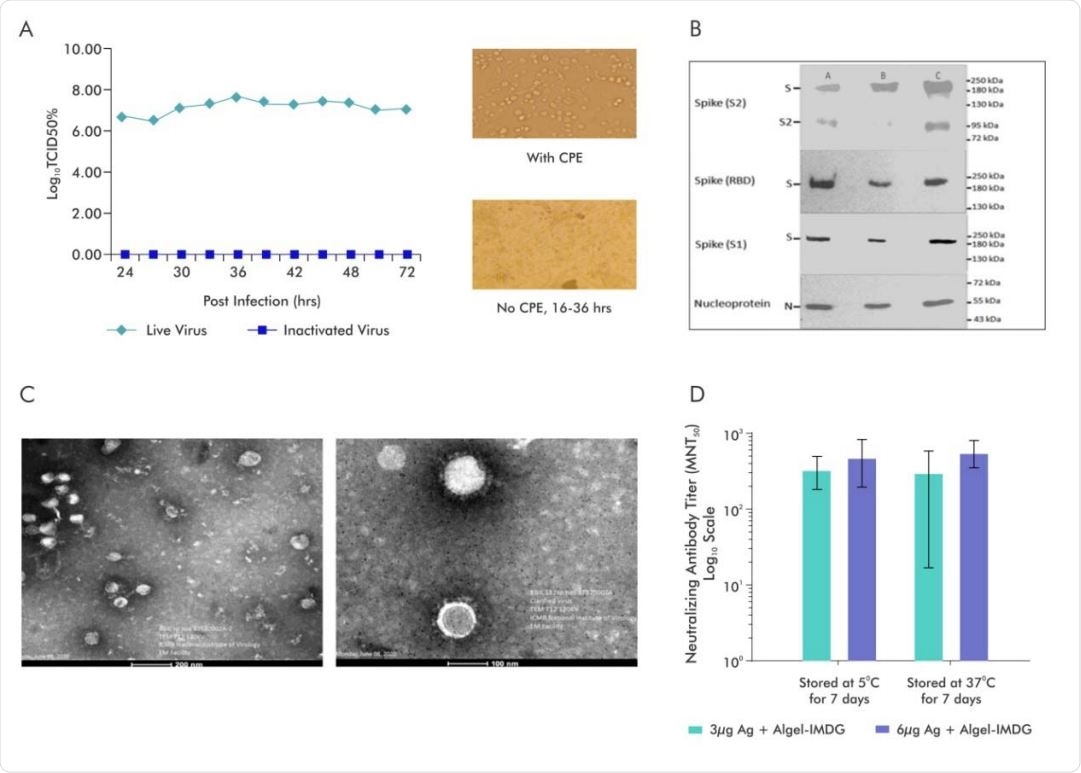
A.SARS-CoV-2 Virus (Strain NIV-770-2020) Growth Kinetics & Cytopathic effect (CPE) of virus before and after Inactivation (i) Virus titer (106 -107 ) measured by CCID50 at every 3 hours up to 48 and after that every 12hrs various time points (24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42), (ii) Cells with Cytopathic Effect (CPE) before inactivation and No CPE after Inactivation, (iii) Image of Vero cell monolayer with no CPE observed from 16-36hrs; B. Representative electron micrograph of purified inactivated SARS-CoV-2 candidate vaccine (BBV152) at a scale bar: 100 nm (right) and 200 nm (left); C. Western blot analysis of Purified Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 produced from three production batches; D.Microneutralization antibody titer of Day 14 sera collected from mice vaccinated with Adjuvanted formulations (3µg Ag with Algel-IMDG and 6µg Ag with AlgelIMDG), after subjecting them for stability at 37°C for 7 days and compared with 2-8°C
Researchers globally are racing to develop an effective vaccine
Since the first cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection were first identified in Wuhan, China, late last year, the virus has spread to almost every country in the world and infected more than 28.7 million people.
Researchers globally are racing to develop both preventive and therapeutic agents that will help to bring the pandemic under control.
A number of vaccines are currently in various stages of preclinical and clinical trials, but producing the billions of doses needed globally will require a collective effort to validate and manufacture effective vaccines, says the team.
Inactivated virions have been licensed as safe vaccines for decades, and the availability of well-established vero cell manufacturing platforms for testing these agents has helped to expedite vaccine development.
Now, Vadrevu and colleagues have used a well-characterized strain of SARS-CoV-2 and an established vero cell platform called CCL-81 to generate large-scale good manufacturing practice (GMP) grade, highly purified BBV152.
An important challenge is Th-2-like immunity
One important challenge researchers face when developing a safe coronavirus vaccine is the vaccine-induced disease that occurs in animal models when Th2-like immunity develops.
The authors say some preclinical studies of inactivated SARS-CoV-1 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) adjuvanted with alum have resulted in Th2 responses that cause eosinophilic infiltration in the lungs.
This type of agonist induces a potent type I interferon response from dendritic cells and monocyte-macrophages that help to drive Th1-biased immunity rather than the pathogenic Th2-biased immunity, explains the team.
The vaccines were effective and safe
The BBV152 vaccine with the two different adjuvants was administered to rats, rabbits, and mice at concentrations of 3µg and 6µg.
At both concentrations, the vaccine-induced the production of high antigen-binding and neutralizing antibody titers in all three animal models.
The neutralizing antibody titers did not statistically differ between the 3µg and 6µg concentrations or between the two types of adjuvant use, with all formulations exhibiting excellent immunogenicity, says the team.
However, the formulation containing the TLR7/8 agonist also induced Th1-biased antibody responses with an elevated immunoglobulin 2a (IgG2a)-to-IgG1 ratio and increased levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific IFN-γ+ CD4 T cells.
Safety testing showed no pathological changes or systemic toxicity and only minimal to no adverse events.
The only side effect observed was a local reaction that is consistent with the reaction previously described in the literature for these adjuvants. Vadrevu and colleagues say the reaction is a physiological response to injection rather than an adverse event.
The findings support further development of the vaccine for clinical trials
“Our results support further development for Phase I/II clinical trials in humans,” concludes the team.“Our results show that these vaccine formulations induced significantly elevated titers of antigen binding and neutralizing antibodies in all animal models tested without any safety concerns,” write the researchers.
*Important Notice
bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
Journal reference:
- Vadrevu K M, et al. Evaluation of Safety and Immunogenicity of an Adjuvanted, TH-1 Skewed, Whole Virion InactivatedSARS-CoV-2 Vaccine - BBV152. bioRxiv 2020. doi: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.09.09.285445v2