Signs of alien life detected on Venus
by Maddie Goodfellow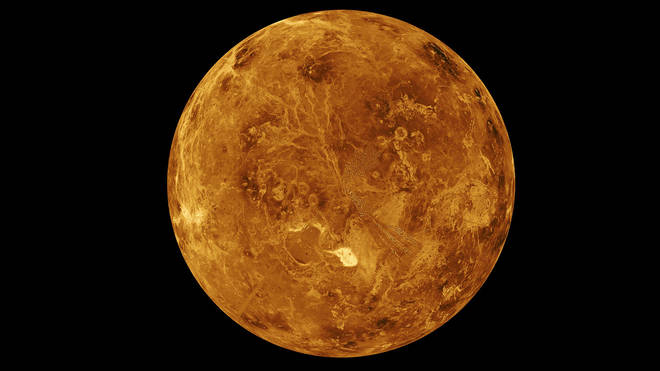
By Maddie Goodfellow
The discovery of phosphine gas in the clouds of Venus could possibly indicate signs of life on the planet, scientists have said.
The gas has been detected in the atmosphere of Venus, suggesting the planet could host unknown photochemical or geochemical processes.
On Earth, phosphine - a colourless gas that has the smell of garlic or decaying fish - is produced predominantly by anaerobic biological sources.
Small amounts of the gas occur naturally from the breakdown of organic matter.
While the conditions on the surface of Venus - the second planet from the Sun - are hostile to life, the environment of its upper cloud deck, around 53-62km (33-38 miles) above the surface, is temperate.
But according to the study, published in Nature Astronomy, the make-up of the clouds is highly acidic, and in such conditions phosphine would be destroyed very quickly.
Jane Greaves, from Cardiff University, and colleagues observed Venus with the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array in 2017 and 2019, respectively.
They detected a spectral signature that is unique to phosphine, and estimated an abundance of 20 parts-per-billion of phosphine in Venus's clouds.
Researchers looked at different ways the gas may have been produced, including from sources on the surface of the planet, micrometeorites, lightning, or chemical processes happening within the clouds.
But they were unable to determine the source of the trace quantities of phosphine.
However, they argue that the detection of phosphine is not robust evidence for microbial life and only indicates potentially unknown geological or chemical processes occurring on the planet.
They say further observations and modelling are needed to explore the origin of the gas in the planet's atmosphere.
Writing in the paper, they say: "PH3 (phosphine) could originate from unknown photochemistry or geochemistry, or, by analogy with biological production of PH3 on Earth, from the presence of life."
They add: "If no known chemical process can explain PH3 within the upper atmosphere of Venus, then it must be produced by a process not previously considered plausible for Venusian conditions.
"This could be unknown photochemistry or geochemistry, or possibly life."
The researchers continue: "Even if confirmed, we emphasise that the detection of PH3 is not robust evidence for life, only for anomalous and unexplained chemistry.
"There are substantial conceptual problems for the idea of life in Venus's clouds - the environment is extremely dehydrating as well as hyperacidic.
"However, we have ruled out many chemical routes to PH3, with the most likely ones falling short by four to eight orders of magnitude.
"To further discriminate between unknown photochemical and/or geological processes as the source of Venusian PH3, or to determine whether there is life in the clouds of Venus, substantial modelling and experimentation will be important.
"Ultimately, a solution could come from revisiting Venus for in situ measurements or aerosol return."
Associate Professor Alan Duffy, an astronomer from Swinburne University and the lead scientist of The Royal Institution of Australia, said: "This is one of the most exciting signs of the possible presence of life beyond Earth I have ever seen, and certainly from the most surprising location I could imagine.
"Our twin planet Venus is a hellish world. While the surface is hot enough to melt lead, the temperature drops as you go higher into the clouds, becoming Earth-like in both temperature and pressure by an altitude of 50km, exactly where the phosphine was found.
"While the temperature is benign the clouds contain sulfuric acid which should break down the phosphine, so something is forming it anew, and as phosphine is associated with life on Earth it is tempting to think it could be life on Venus.
"But before we can become more confident about that we have to rule out all possible other non-biological means of producing it."